An abscessed tooth often starts quietly but can quickly affect daily life, causing persistent pain, facial swelling, sleep disruption, and unexpected health concerns that should never be ignored. Have you ever felt a toothache that seemed deeper than usual and refused to fade? Many people describe it as a throbbing pressure that comes and goes. Others notice swelling or a strange taste without clear explanation. These early signs often point toward an abscessed tooth. Understanding what this condition means helps reduce fear and delays. Awareness encourages timely action before complications develop.
What exactly is an abscessed tooth?
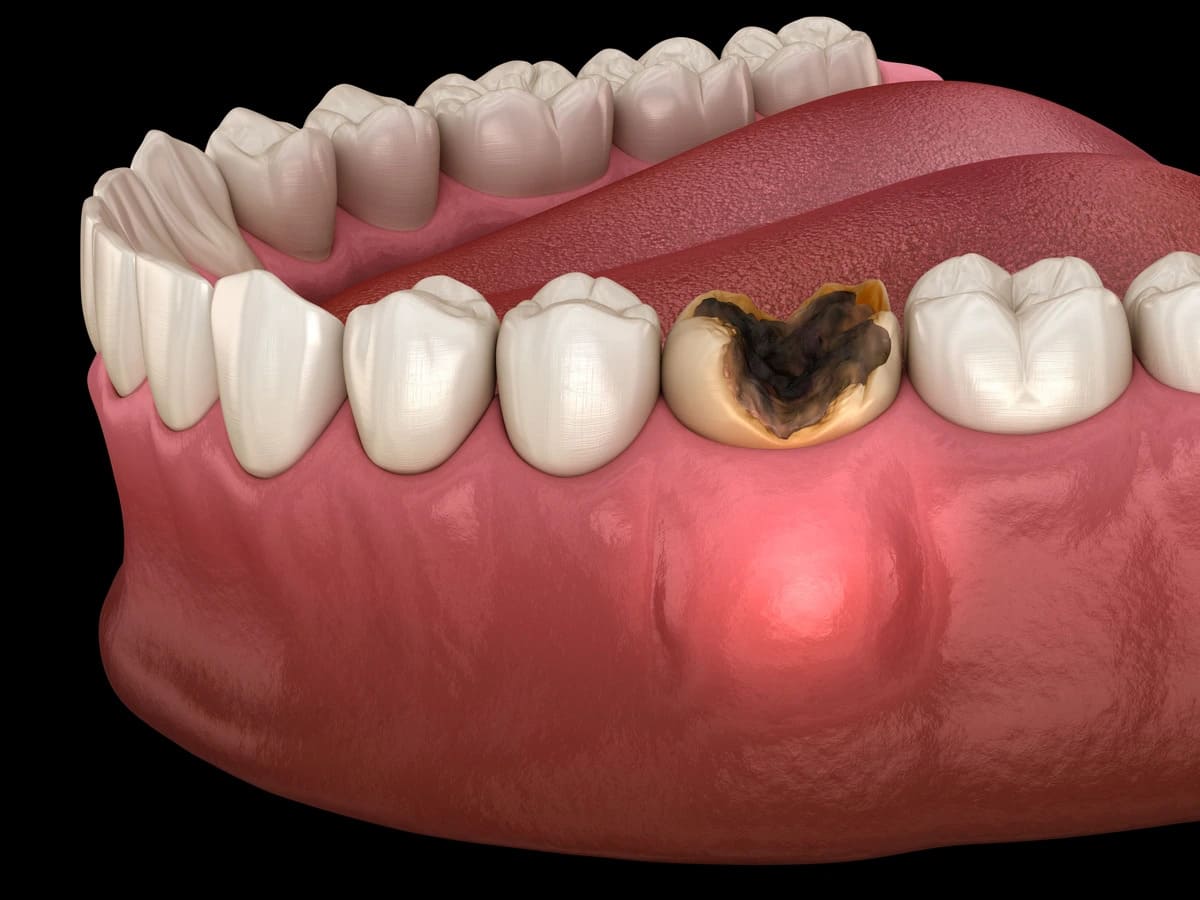
An abscessed tooth is an infection located at the root of the tooth or surrounding gum tissue. It forms when bacteria enter deep tooth structures and multiply. This infection creates a pocket of pus that builds pressure over time. Pain often becomes persistent and intense as pressure increases. According to our editor’s research, abscesses rarely heal without professional intervention. The condition usually reflects advanced dental decay or untreated trauma. Ignoring it allows infection to spread further. Early understanding supports faster and safer response.
How does a tooth become abscessed?
Bacteria usually enter through untreated cavities or microscopic cracks in enamel. Poor oral hygiene increases this risk gradually over time. Dental trauma may expose the inner layers of the tooth. Previous dental work can sometimes weaken tooth structure. Gum disease also allows bacteria to reach deeper tissues. As a result of our editor’s reviews, decay remains the most common cause. Once bacteria reach the pulp, infection develops rapidly. Limited blood supply prevents natural healing.
Why does an abscess cause so much pain?
Pain develops due to pressure buildup inside confined spaces within the tooth. Nerve tissue reacts strongly to inflammation and swelling. Pressure compresses surrounding structures and nerves. Pain may radiate toward the jaw, ear, or head. Sensitivity often increases with hot or cold exposure. According to our editor’s observations, pain severity varies widely between patients. Some feel constant throbbing while others experience sharp bursts. Pain often worsens during nighttime rest.
What symptoms commonly appear first?
Tooth sensitivity is often an early warning sign. Persistent aching replaces brief discomfort over time. Swelling near the affected tooth may become visible. Gums can appear red, shiny, or tender. A bitter or metallic taste may be noticeable. According to our editor’s research, taste changes are frequently overlooked. Bad breath may accompany the infection. Chewing becomes increasingly uncomfortable. Symptoms usually intensify without treatment.
Can an abscess affect areas beyond the tooth?
Infection can spread to surrounding facial tissues. Swelling may extend to the cheek or jawline. Jaw stiffness can limit normal mouth opening. Lymph nodes in the neck may enlarge. Fever may signal systemic involvement. As a result of our editor’s reviews, spread risk increases with treatment delay. Severe cases may involve sinuses or jawbone. Rarely, infection can enter the bloodstream. Prompt care prevents these serious outcomes.
How is an abscessed tooth diagnosed?
Dentists begin with a detailed discussion of symptoms. Visual examination identifies swelling, decay, or gum changes. Dental X-rays reveal infection depth and bone involvement. Gentle tapping tests tooth sensitivity. Temperature tests assess nerve vitality. According to our editor’s experience, imaging confirms severity clearly. Accurate diagnosis guides appropriate treatment choice. Early detection limits complications. Clear explanation reassures patients.
What treatment options are commonly used?
Treatment focuses on eliminating the infection source. Drainage reduces pressure and pain quickly. Root canal therapy removes infected pulp tissue. Severely damaged teeth may require extraction. Antibiotics help control bacterial spread. According to our editor’s research, antibiotics alone are never sufficient. Definitive dental treatment remains essential. Pain relief follows infection control. Treatment plans vary by severity.
Why antibiotics are not a complete solution
Antibiotics reduce bacterial spread temporarily. They cannot remove infected tissue from inside the tooth. Pus pockets limit medication effectiveness. Symptoms may briefly improve then return. Infection usually persists without dental procedures. As a result of our editor’s reviews, reliance on antibiotics delays healing. Antibiotics support but do not replace intervention. Proper treatment resolves the root cause. Understanding this prevents false reassurance.
What happens during a root canal?
Root canal therapy removes infected pulp from the tooth interior. The canals are cleaned and shaped carefully. Disinfection eliminates remaining bacteria. The tooth is sealed to prevent reinfection. Structure is preserved whenever possible. According to our editor’s observations, modern techniques reduce discomfort significantly. Pain relief often follows quickly. The tooth remains functional. Recovery is usually smooth.
When is tooth extraction necessary?
Extraction becomes necessary when damage is extensive. Cracks may compromise structural integrity. Severe decay weakens tooth support. Recurrent infections influence decisions. Bone loss around the tooth also matters. As a result of our editor’s reviews, extraction is considered a last resort. Removal eliminates the infection source completely. Replacement options are discussed later. Timely care prevents spread.
How urgent is treatment for an abscess?
Abscesses require prompt professional attention. Pain escalation often signals progression. Delays increase the risk of complications. Emergency symptoms include fever or rapid swelling. Difficulty swallowing requires urgent care. According to our editor’s research, timing strongly affects outcomes. Early visits simplify treatment. Late visits increase complexity. Urgency should not be underestimated.
Can an abscess heal on its own?
Abscesses almost never resolve without treatment. Pain may temporarily lessen but infection remains. Drainage alone does not equal healing. Symptoms often return more severe. As a result of our editor’s reviews, self resolution is extremely uncommon. Delaying care worsens damage. Professional treatment is essential. Awareness prevents dangerous assumptions.
How does oral hygiene influence risk?
Daily brushing removes harmful bacteria effectively. Flossing cleans areas brushes cannot reach. Regular dental checkups detect early decay. Diet choices influence bacterial growth. Sugar intake increases cavity risk. According to our editor’s experience, prevention is highly effective. Consistency matters more than perfection. Good habits reduce abscess likelihood. Prevention supports long term health.
Are certain people more at risk?
People with untreated cavities face higher risk. Those avoiding dental visits are more vulnerable. Dry mouth conditions increase susceptibility. Chronic illness may weaken immune response. Smoking worsens gum health significantly. As a result of our editor’s research, multiple factors interact. Risk accumulates gradually over time. Awareness supports prevention. Personal risk assessment matters.
What complications can occur if untreated?
Infection may spread to the jawbone. Sinus involvement causes facial pressure. Facial cellulitis can develop rapidly. Systemic infection poses serious risks. Hospitalization may become necessary. According to our editor’s reviews, severe outcomes are preventable. Early care reduces danger. Complications reflect delay rather than inevitability. Education changes outcomes.
How long does recovery usually take?
Pain relief often begins quickly after treatment. Swelling typically reduces within days. Healing continues internally over weeks. Follow-up visits monitor progress. Full recovery varies by individual. Our editor’s observations show improvement within weeks. Adherence to instructions matters greatly. Medications support healing. Patience ensures success.
Can children develop abscessed teeth?
Children can develop abscesses as well. Baby teeth are not immune. Decay progresses faster in children. Pain expression may be subtle. Swelling signals urgency. According to our editor’s research, pediatric abscesses need prompt care. Early treatment protects permanent teeth. Education supports prevention. Parents should monitor symptoms closely.
How does an abscess affect daily life?
Pain disrupts normal sleep patterns. Eating becomes uncomfortable or avoided. Concentration and mood may suffer. Social interactions feel challenging. Work performance can decline noticeably. As a result of our editor’s reviews, quality of life impact is significant. Timely care restores normal routines. Relief improves wellbeing. Oral health supports productivity.
What myths surround abscessed teeth?
Some believe pain will fade permanently on its own. Others fear treatment more than infection. Home remedies offer false reassurance. Drainage alone does not cure infection. Ignoring symptoms worsens outcomes. According to our editor’s experience, myths delay care. Education corrects misconceptions. Facts empower action. Knowledge replaces fear.
When should someone see a dentist immediately?
Persistent tooth pain requires evaluation. Swelling demands urgent attention. Fever may signal infection spread. Difficulty opening the mouth is concerning. Bad taste with pain often indicates pus. As a result of our editor’s research, early visits simplify care. Waiting complicates treatment. Prompt response protects health. Awareness saves teeth.
How can future abscesses be prevented?
Regular dental visits detect early problems. Good hygiene limits bacterial growth. Treating cavities promptly prevents spread. Protective treatments strengthen enamel. Lifestyle choices influence oral health. According to our editor’s observations, prevention remains effective. Small habits yield big benefits. Consistency reduces risk. Prevention supports confidence.
